分枝桿菌屬
此條目可參照英語維基百科相應條目來擴充。 |
分枝桿菌屬(學名:Mycobacterium)為放線菌門的一屬細菌,且為分枝桿菌科唯一的屬。為形狀不規則的革蘭氏陽性桿菌,不能游動,通常抗酸,無氣生菌絲和孢子。
| 分枝桿菌屬 | |
|---|---|
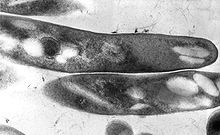
| |
| 結核分枝桿菌 | |
| 科學分類 | |
| 域: | 細菌域 Bacteria |
| 門: | 放線菌門 Actinomycetota |
| 綱: | 放線菌綱 Actinomycetes |
| 目: | 分枝桿菌目 Mycobacteriales |
| 科: | 分枝桿菌科 Mycobacteriaceae |
| 屬: | 分枝桿菌屬 Mycobacterium Lehmann & Neumann 1896 |
| 模式種 | |
| Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Zopf 1883) Lehmann and Neumann 1896
| |
該屬細菌包括許多已知在哺乳類動物中造成嚴重疾病的病原菌,包括結核桿菌(Mycobacterium tuberculosis)和麻風桿菌(Mycobacterium leprae)[1]。
希臘語中的 myco 表示「真菌」,意思是說該屬的物種通常在液態培養基的表面,形成類似黴菌的菌落。[2]
2018年,基於全基因組測序的數據,對分枝桿菌屬進一步進行修訂,並拆分出4個新的菌屬,即Mycolicibacillus、Mycolicibacter、Mycobacteroides和Mycolicibacterium。[3]
微生物特徵
編輯1. 外層脂質
2. mycolic acid
3. 多醣(arabinogalactan)
4. 肽聚糖
5. 細胞膜
6. lipoarabinomannan(LAM)
7. phosphatidylinositol mannoside
8. 細胞壁骨架
本屬物種為好氧型細菌,且為不運動型細菌(海洋分枝桿菌除外,其可以在巨噬細胞內運動),為一種抗酸型細菌[1]。分枝桿菌並不會形成內孢子或莢膜,因此常被認定為革蘭氏陰性菌。且分枝桿菌在革蘭氏染色上並無法染上結晶紫,因此無法被歸類於革蘭氏陽性菌或陰性菌。
雖然說本屬不產孢子,但有兩個物種似乎例外,那就是海洋分枝桿菌(Mycobacterium marinum)和牛分枝桿菌(M. bovis)[4]。但進一步的研究引發了爭論。[5]
分枝桿菌的特點就是其細胞壁較其他物種厚,且呈蠟狀疏水性,並含有大量的分枝菌酸(mycolic acids)。多醣會將分枝菌酸層及肽聚糖層拉在一起,讓細胞壁變得十分堅韌。若可干擾其細胞壁的生物合成途徑,也許可以開發治療肺結核的藥物。[6]
物種
編輯表型測試可用於識別和區分不同的分枝桿菌物種和菌株。在以前的系統中,分枝桿菌根據它們的外觀和生長速度進行分組的。然而,這些是近祖共性(symplesiomorphies)的,並且最近的分類基於支序分類學(cladistics)進行的。
慢速生長菌
編輯- Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex (MTBC) members are causative agents of human and animal tuberculosis. Species in this complex include:
- Mycobacterium avium complex (MAC) is a group of species that, in a disseminated infection but not lung infection, used to be a significant cause of death in AIDS patients. The species M. indicus pranii appears to be basal in this complex.[9]Species in this complex include:
- M. avium
- 鳥分枝桿菌類結核亞種 M. avium paratuberculosis, which has been implicated in Crohn's disease in humans and is the causative agent of Johne's disease in cattle and sheep
- M. avium silvaticum
- M. avium "hominissuis"
- 哥倫比亞分枝桿菌 M. colombiense
- M. indicus pranii
堪薩斯分支桿菌支序群 (Mycobacterium kansasii clade)
編輯無色分枝桿菌/土分枝桿菌支序群 Mycobacterium nonchromogenicum/terrae clade
編輯Mycolactone-producing mycobacteria
編輯- 潰瘍分枝桿菌 Mycobacterium ulcerans MacCallum et al. 1950 , 其會引起布如里氏潰瘍("Buruli"), 或 "Bairnsdale, ulcer"]]
- 假分枝桿菌 Mycobacterium pseudoshottsii Rhodes et al. 2005
- Mycobacterium shottsii Rhodes et al. 2003
猴分枝桿菌支序群 Mycobacterium simiae clade
編輯- 三重分枝桿菌 M. triplex
- 日內瓦分枝桿菌 M. genavense
- 佛羅倫薩分枝桿菌 M. florentinum
- 緩黃分枝桿菌 M. lentiflavum
- 沼澤分枝桿菌 M. palustre
- M. kubicae
- M. parascrofulaceum
- 海德堡分枝桿菌 M. heidelbergense
- 居間分枝桿菌 M. interjectum
- 猴分枝桿菌 M. simiae
未分群
編輯- 德氏分枝桿菌 M. branderi
- M. cookii
- 隱藏分枝桿菌 M. celatum
- M. bohemicum
- 嗜血分枝桿菌 M. haemophilum
- 瑪爾摩分枝桿菌 M. malmoense
- 蘇加分枝桿菌 M. szulgai
- 痲瘋桿菌 Mycobacterium leprae,麻風分枝桿菌, 痲瘋病的致病菌
- 鼠麻風分枝桿菌 M. lepraemurium
- M. lepromatosis (M. lepromatosis) 另一種引起痲瘋病的較少見致病菌,於2008年被描述
- 博氏分票桿菌 Mycobacterium botniense
- 嵌合分枝桿菌 M. chimaera
- 出眾分枝桿菌 M. conspicuum
- M. doricum
- 鼻疽分枝桿菌 M. farcinogenes
- 半島分枝桿菌 M. heckeshornense
- 胞內分枝桿菌 M. intracellulare
- 洛克司分枝桿菌 M. lacus
- 海洋分枝桿菌(M. marinum), causes a rare disease called Aquarium granuloma.
- M. monacense
- 摩特弗分枝桿菌 M. montefiorense
- M. murale
- 內布拉斯加分枝桿菌 M. nebraskense
- 薩斯喀徹溫分枝桿菌 M. saskatchewanense
- 瘰病分枝桿菌 M. scrofulaceum
- M. shimoidei
- 托斯卡納分枝桿菌 M. tusciae
- 蟾分枝桿菌 M. xenopi
- M. yongonense
生長速率中等
編輯- Mycobacterium intermedium Meier et al. 1993
快速生長菌
編輯龜分枝桿菌支序群 Mycobacterium chelonae clade
編輯偶然分枝桿菌群 Mycobacterium fortuitum clade
編輯- 偶然分枝桿菌 Mycobacterium fortuitum
- Mycobacterium fortuitum subsp. acetamidolyticum
- Mycobacterium boenickei
- Mycobacterium peregrinum
- 豬分枝桿菌 Mycobacterium porcinum
- 塞內加爾分枝桿菌 Mycobacterium senegalense
- 敗血分枝桿菌 Mycobacterium septicum
- Mycobacterium neworleansense
- 休斯頓分枝桿菌 Mycobacterium houstonense
- 產黏液分枝桿菌 Mycobacterium mucogenicum
- 馬德里分枝桿菌 Mycobacterium mageritense
- Mycobacterium brisbanense
- Mycobacterium cosmeticum
Mycobacterium parafortuitum 支序群
編輯- M. parafortuitum
- 南非分枝桿菌 M. austroafricanum
- M. diernhoferi
- M. hodleri
- 新金色分枝桿菌 M. neoaurum
- M. frederiksbergense
Mycobacterium vaccae 支序群
編輯CF
編輯未分群
編輯- Mycobacterium agri
- Mycobacterium aichiense
- Mycobacterium alvei
- Mycobacterium arupense
- Mycobacterium brumae
- Mycobacterium canariasense
- Mycobacterium chubuense
- 康賽醫院分枝桿菌 Mycobacterium conceptionense
- Mycobacterium confluentis Kirschner et al. 1992
- Mycobacterium duvalii
- 象分枝桿菌 Mycobacterium elephantis
- Mycobacterium flavescens Bojalil et al. 1962
- Mycobacterium gadium
- Mycobacterium gilvum
- 古地分枝桿菌 Mycobacterium goodii
- Mycobacterium hassiacum
- Mycobacterium holsaticum
- 免疫原分枝桿菌 Mycobacterium immunogenum
- Mycobacterium komossense
- 馬達加斯加分枝桿菌 Mycobacterium madagascariense
- 馬賽分枝桿菌 Mycobacterium massiliense
- Mycobacterium moriokaense Tsukamura et al. 1986
- 大府分枝桿菌 Mycobacterium obuense ,也拼作:Mycobacterium obuense
- 草分枝桿菌 Mycobacterium phlei Lehmann and Neumann 1899
- Mycobacterium psychrotolerans
- Mycobacterium pulveris
- Mycobacterium pyrenivorans
- 包皮垢分枝桿菌 Mycobacterium smegmatis (Trevisan 1889) Lehmann and Neumann 1899,恥垢分枝桿菌
- 泥炭蘚分枝桿菌 Mycobacterium sphagni Kazda 1980
- Mycobacterium thermoresistibile
- Mycobacterium vanbaalenii
- 沃氏分枝桿菌 Mycobacterium wolinskyi
未分群
編輯- Mycobacterium arosiense
- 歐巴涅分枝桿菌 Mycobacterium aubagnense
- 山羊分枝桿菌 Mycobacterium caprae
- Mycobacterium chlorophenolicum
- Mycobacterium fluoroanthenivorans
- Mycobacterium kiyosense Fukano et al. 2023[11]
- Mycobacterium kumamotonense Masaki et al. 2007
- 新城分枝桿菌 Mycobacterium novocastrense Shojaei et al. 1997
- 帕爾門塞分枝桿菌 Mycobacterium parmense
- 弗卡分枝桿菌 Mycobacterium phocaicum
- Mycobacterium poriferae
- Mycobacterium rhodesiae
- Mycobacterium salfingeri Musser et al. 2024[12]
- Mycobacterium seoulense
- Mycobacterium tokaiense
分枝桿菌噬菌體
編輯參見
編輯參考文獻
編輯- ^ 1.0 1.1 Ryan KJ, Ray CG (editors). Sherris Medical Microbiology 4th. McGraw Hill. 2004. ISBN 0-8385-8529-9.
- ^ James H. Kerr and Terry L. Barrett, "Atypical Mycobacterial Diseases", Military Dermatology Textbook, p. 401.
- ^ Gupta RS, Lo B, Son J. Phylogenomics and Comparative Genomic Studies Robustly Support Division of the Genus Mycobacterium into an Emended Genus Mycobacterium and Four Novel Genera. Front Microbiol 2018; 9:67.
- ^ Ghosh, Jaydip; Larsson, Pontus; Singh, Bhupender; Pettersson, B. M. Fredrik; Islam, Nurul M.; Sarkar, Sailendra Nath; Dasgupta, Santanu; Kirsebom, Leif A. Sporulation in mycobacteria. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 2009-06-30, 106 (26). ISSN 0027-8424. PMC 2705590 . PMID 19541637. doi:10.1073/pnas.0904104106 (英語).
- ^ Traag BA, Driks A, Stragier P, Bitter W, Broussard G, Hatfull G, Chu F, Adams KN, Ramakrishnan L, Losick R.2010. "Do mycobacteria produce endospores?" Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Jan 12;107(2):878-81.
- ^ Bhamidi S. Mycobacterial Cell Wall Arabinogalactan. Bacterial Polysaccharides: Current Innovations and Future Trends. Caister Academic Press. 2009. ISBN 978-1-904455-45-5.
- ^ 7.0 7.1 术语在线—权威的术语知识服务平台. www.termonline.cn. [2022-08-02].
- ^ 國家教育研究院雙語詞彙、學術名詞暨辭書資訊網. terms.naer.edu.tw. [2022-08-02].
- ^ Rahman, Syed Asad; Singh, Yadvir; Kohli, Sakshi; Ahmad, Javeed; Ehtesham, Nasreen Z.; Tyagi, Anil K.; Hasnain, Seyed E. Lee, Sang Yup , 編. Comparative Analyses of Nonpathogenic, Opportunistic, and Totally Pathogenic Mycobacteria Reveal Genomic and Biochemical Variabilities and Highlight the Survival Attributes of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. mBio. 2014-12-31, 5 (6) [2022-08-02]. ISSN 2161-2129. PMC 4222108 . PMID 25370496. doi:10.1128/mBio.02020-14. (原始內容存檔於2022-06-25) (英語).
- ^ clade - 支序群;分支群;分支. [2021-04-09]. (原始內容存檔於2021-04-21).
- ^ Fukano H, Kazumi Y, Sakagami N, Fujiwara N, Ato M, Mitarai S, Hoshino Y. Mycobacterium kiyosense sp. nov., a scotochromogenic slow-glowing species isolated from respiratory specimens. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 2023; 73:5917.
- ^ Musser E, Smith C, Halse TA, Kohlerschmidt D, Rourke A, Fiero A, Musser KA, Escuyer V, Lapierre P. Characterization of Mycobacterium salfingeri sp. nov.: A novel nontuberculous mycobacteria isolated from a human wound infection. Front Microbiol 2022; 13:992610.
延伸閱讀
編輯- Diagnosis and Treatment of Disease Caused by Nontuberculous Mycobacteria (頁面存檔備份,存於網際網路檔案館). American Thoracic Society. Am J Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine. Aug 1997 156(2) Part 2 Supplement
- RIDOM: Ribosomal Differentiation of Medical Microorganisms
- J.P. Euzéby: List of Prokaryotic Names with Standing in Nomenclature - Genus Mycobacterium
外部連結
編輯- Tuberculist (頁面存檔備份,存於網際網路檔案館): Genome annotation database
- MTB Sysborg: Genome annotation database from the Institute of Genomics and Integrative Biology
- TB Structural Genomics Consortium: Structures of Mycobacterium tuberculosis proteins
- MycDB: Mycobacterium database
- TBDB: Tuberculosis database
- Mycobacteriumgenomes and related information at PATRIC(頁面存檔備份,存於網際網路檔案館), a Bioinformatics Resource Center funded by NIAID(頁面存檔備份,存於網際網路檔案館)
- Frequently Asked Questions about NTM Lung Disease
- PRASITE: Identification of mycobacteria (頁面存檔備份,存於網際網路檔案館)
template:Gram-positive actinobacteria diseases template:Mycobacteria