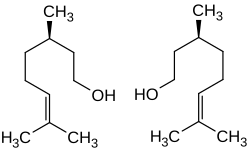
香茅醇
香茅醇(Citronellol)是一种天然有机化合物,存在于多种植物精油以及一些水果中,属于类萜。其两种对映异构体在自然界中均有分布:R-(+)-香茅醇, 存在于香茅油 (50%);而S-(−)-香茅醇存在于蔷薇属植物精油中(18–55%),以及天竺葵属植物等。[1]
| 香茅醇 | |
|---|---|
| |
| |
| |
| IUPAC名 3,7-Dimethyloct-6-en-1-ol | |
| 别名 | (±)-β-Citronellol; 3,7-Dimethyl-6-octen-1-ol |
| 识别 | |
| CAS号 | 106-22-9 |
| ChemSpider | 13850135 |
| SMILES |
|
| InChI |
|
| InChIKey | QMVPMAAFGQKVCJ-SNVBAGLBBU |
| ChEBI | 50462 |
| KEGG | C09849 |
| 性质 | |
| 化学式 | C10H20O |
| 摩尔质量 | 156.27 g·mol−1 |
| 密度 | 0.855 g/cm3 |
| 沸点 | 225 °C(498 K) |
| 危险性 | |
| NFPA 704 | |
| 若非注明,所有数据均出自标准状态(25 ℃,100 kPa)下。 | |
制备
编辑每年生产数百万公斤的香茅醇。 香茅醇主要由香叶醇或橙花醇在亚铬酸铜催化剂上加氢化合成[2]。 均相催化劑用于生产对映异构体[3][4]。
应用
编辑香茅醇用于香水和驱虫剂,[5]农业害螨引诱剂。[6]香茅醇在短距离内是一种很好的驱蚊剂,但保护性能随距离增加大大降低。[7]与环糊精结合能增强驱蚊效用,有效时间提升至1.5小时。[8]
健康和安全性
编辑美国食品药品监督管理局(FDA)将香茅醇归入“公认安全”(GRAS)的分类,[6]在食物中仅限作为香料用途添加。[10]有报道称一些人群可能对香茅醇敏感,但其作为食品添加剂时的剂量是否足以使人过敏则尚不清楚。[11][12]
就皮肤安全性而言,香茅醇已被评估为一种驱虫剂[13] 。
参见
编辑参考资料
编辑- ^ Lawless, J. The Illustrated Encyclopedia of Essential Oils. ISBN 1-85230-661-0.
- ^ Sell, Charles S. Terpenoids. Kirk-Othmer Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology. 2006. ISBN 0471238961. doi:10.1002/0471238961.2005181602120504.a01.pub2.
- ^ Morris, Robert H. Ruthenium and Osmium. De Vries, J. G.; Elsevier, C. J. (编). The Handbook of Homogeneous Hydrogenation. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. 2007. ISBN 978-3-527-31161-3.
- ^ Ait Ali, M.; Allaoud, S.; Karim, A.; Roucoux, A.; Mortreux, A. Catalytic Synthesis of (R)- and (S)-citronellol by homogeneous hydrogenation over amidophosphinephosphinite and diaminodiphosphine rhodium complexes. Tetrahedron: Asymmetry. 1995, 6 (2): 369. doi:10.1016/0957-4166(95)00015-H.
- ^ Taylor WG, Schreck CE. Chiral-phase capillary gas chromatography and mosquito repellent activity of some oxazolidine derivatives of (+)- and (−)-citronellol. J Pharm Sci. 1985, 74 (5): 534–539. PMID 2862274. doi:10.1002/jps.2600740508.
- ^ 6.0 6.1 Citronellol (167004) Fact Sheet (PDF). epa.gov. [12 May 2017]. (原始内容存档 (PDF)于2017-04-30). (页面存档备份,存于互联网档案馆)
- ^ Revay, Edita E.; Kline, Daniel L.; Xue, Rui-De; Qualls, Whitney A.; Bernier, Ulrich R.; Kravchenko, Vasiliy D.; Ghattas, Nina; Pstygo, Irina; Müller, Günter C. Reduction of mosquito biting-pressure: Spatial repellents or mosquito traps? A field comparison of seven commercially available products in Israel. Acta Tropica. 2013, 127 (1): 63–8. PMID 23545129. doi:10.1016/j.actatropica.2013.03.011.
- ^ Songkro, Sarunyoo; Hayook, Narissara; Jaisawang, Jittarat; Maneenuan, Duangkhae; Chuchome, Thitima; Kaewnopparat, Nattha. Investigation of inclusion complexes of citronella oil, citronellal and citronellol with β-cyclodextrin for mosquito repellent. Journal of Inclusion Phenomena and Macrocyclic Chemistry. 2011, 72 (3–4): 339. doi:10.1007/s10847-011-9985-7.
- ^ “Dark” Singlet Oxygenation of β-Citronellol: A Key Step in the Manufacture of Rose Oxide. Organic Process Research & Development.
- ^ 存档副本. [2012-07-19]. (原始内容存档于2012-01-06). (页面存档备份,存于互联网档案馆)
- ^ Cropwatch Report April 2008 (PDF). [2017-05-12]. (原始内容 (PDF)存档于2014-02-10). (页面存档备份,存于互联网档案馆)
- ^ Survey and health assessment of chemical substances in massage oils 互联网档案馆的存檔,存档日期2007-09-27.
- ^ Taylor, W. G.; Schreck, C. E. Chiral-phase capillary gas chromatography and mosquito repellent activity of some oxazolidine derivatives of (+)- and (−)-citronellol. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences. 1985, 74 (5): 534–539 [2023-05-21]. PMID 2862274. doi:10.1002/jps.2600740508. (原始内容存档于2022-12-01). (页面存档备份,存于互联网档案馆)
