阿莫雷生
化合物
阿莫雷生(英语:Almorexant;开发代号:ACT-078573),或译阿莫伦特,是一种食欲素拮抗剂,可作为食欲素受体(OX1和OX2)的竞争性拮抗剂。该药物由制药公司Actelion和葛兰素史克开发,用于治疗失眠。[3]由于在试验中观察到肝酶短暂升高后对阿莫雷生的肝脏安全性存在担忧,该药物的开发于2011年1月被中止。[4][5]
 | |
| 临床资料 | |
|---|---|
| 其他名称 | ACT-078573 |
| 给药途径 | 口服 |
| 药物类别 | 食欲素拮抗剂 |
| ATC码 |
|
| 药物动力学数据 | |
| 药物代谢 | 肝 |
| 生物半衰期 | 13–19小时[1][2] |
| 识别信息 | |
| |
| CAS号 | 871224-64-5( 913358-93-7 (HCl)) |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| 化学信息 | |
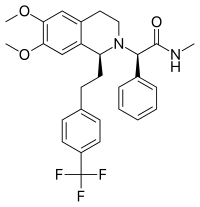
| 化学式 | C29H31F3N2O3 |
| 摩尔质量 | 512.57 g·mol−1 |
| 3D模型(JSmol) | |
| |
| |
药理学
编辑药效学
编辑阿莫雷生是一种竞争性双重OX1和OX2受体拮抗剂,它可选择性抑制OX1和OX2受体激活所产生的功能性后果,例如细胞内Ca2+动员。它与食欲素受体的解离速度非常缓慢,这可能会延长其作用持续时间。[6]
历史
编辑阿莫雷生最初由Actelion开发,从2007年开始被报道为一种潜在的重磅药物,因为其新颖的作用机制(食欲素受体拮抗作用)被认为能产生比传统的苯二氮䓬类药物和Z类药物更好的睡眠质量和更少的副作用。这些传统药物主导了数十亿美元的失眠药物市场。[7]
2008年,葛兰素史克以1.47亿美元的首期付款从Actelion手中购买了阿莫雷生的开发和营销权。[8]如果该药物成功完成临床开发并获得美国食品药品监督管理局批准,这笔交易的价值估计为32亿美元。[9]葛兰素史克和Actelion继续共同开发该药物,并于2009年11月完成了III期临床试验。[10]
参考资料
编辑- ^ Andrews SP, Aves SJ, Christopher JA, Nonoo R. Orexin Receptor Antagonists: Historical Perspectives and Future Opportunities. Current Topics in Medicinal Chemistry. 2016, 16 (29): 3438–3469. PMID 26416477. doi:10.2174/1568026616666150929111607.
- ^ Hoever P, de Haas S, Winkler J, Schoemaker RC, Chiossi E, van Gerven J, Dingemanse J. Orexin receptor antagonism, a new sleep-promoting paradigm: an ascending single-dose study with almorexant. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics. May 2010, 87 (5): 593–600. PMID 20376002. S2CID 37675356. doi:10.1038/clpt.2010.19.
- ^ Neubauer DN. Almorexant, a dual orexin receptor antagonist for the treatment of insomnia. Current Opinion in Investigational Drugs. January 2010, 11 (1): 101–110. PMID 20047164.
- ^ 4.0 4.1 GSK and Actelion discontinue clinical development of almorexant. GSK press release. 28 January 2011. (原始内容存档于2011-07-04).
- ^ Hoch M, van Gorsel H, van Gerven J, Dingemanse J. Entry-into-humans study with ACT-462206, a novel dual orexin receptor antagonist, comparing its pharmacodynamics with almorexant. Journal of Clinical Pharmacology. September 2014, 54 (9): 979–986. PMID 24691844. S2CID 40714628. doi:10.1002/jcph.297.
- ^ Jacobson LH, Hoyer D, de Lecea L. Hypocretins (orexins): The ultimate translational neuropeptides. Journal of Internal Medicine. May 2022, 291 (5): 533–556. PMID 35043499. S2CID 248119793. doi:10.1111/joim.13406.
- ^ Sleeping Beautifully. CBS Business Network. 24 September 2007.
- ^ Actelion Sells Glaxo Almorexant Sleep Medicine Rights. Bloomberg. 14 July 2008 [2024-02-29]. (原始内容存档于2012-11-05).
- ^ Actelion's top dollar deal leaves doubts, and little on the horizon. EP Vantage. 14 July 2008.
- ^ Clinical trial number NCT00608985 for "Almorexant in Adult Subjects With Chronic Primary Insomnia (RESTORA 1)" at ClinicalTrials.gov
- ^ Actelion and GSK Discontinue Clinical Development of Almorexant. Actelion press release. 28 January 2011. (原始内容存档于2011-03-03).
- ^ Cruz, Hans G.; Hoever, Petra; Chakraborty, Bijan; Schoedel, Kerri; Sellers, Edward M.; Dingemanse, Jasper. Assessment of the Abuse Liability of a Dual Orexin Receptor Antagonist: A Crossover Study of Almorexant and Zolpidem in Recreational Drug Users. CNS Drugs. April 2014, 28 (4): 361–372. doi:10.1007/s40263-014-0150-x.