3-甲氧基酪胺
化合物
(重定向自3-甲氧酪胺)
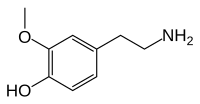
3-甲氧基酪胺(3-MT),或稱3-甲氧基-4-羟基苯乙胺,是一种人体痕量胺,是神经递质多巴胺的代谢产物。[1]通过儿茶酚-O-甲基转移酶(COMT)将一個甲基引入多巴胺而形成。3-MT可进一步被单胺氧化酶(MAO)代谢形成高香草酸(HVA),然后随尿液排出人體。
| 3-甲氧基酪胺 | |
|---|---|
| |

| |
| 别名 | 3-甲氧基-4-羟基苯乙胺 |
| 识别 | |
| CAS号 | 554-52-9 |
| PubChem | 1669 |
| ChemSpider | 1606 |
| InChI |
|
| InChIKey | DIVQKHQLANKJQO-UHFFFAOYAB |
| MeSH | 3-methoxytyramine |
| IUPHAR配体 | 6642 |
| 性质 | |
| 化学式 | C9H13NO2 |
| 摩尔质量 | 167.21 g·mol⁻¹ |
| 若非注明,所有数据均出自标准状态(25 ℃,100 kPa)下。 | |
合成
编辑參見
编辑参考文獻
编辑- ^ 1.0 1.1 The emerging roles of human trace amines and human trace amine-associated receptors (hTAARs) in central nervous system. Biomed. Pharmacother. October 2016, 83: 439–449. PMID 27424325. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2016.07.002.Khan MZ, Nawaz W (October 2016). "The emerging roles of human trace amines and human trace amine-associated receptors (hTAARs) in central nervous system". Biomed. Pharmacother. 83: 439–449. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2016.07.002. PMID 27424325.
- ^ The dopamine metabolite 3-methoxytyramine is a neuromodulator. PLOS ONE. 2010, 5 (10): e13452. Bibcode:2010PLoSO...513452S. PMC 2956650 . PMID 20976142. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0013452.
- ^ Broadley KJ. The vascular effects of trace amines and amphetamines. Pharmacol. Ther. 2010-03, 125 (3): 363–375. PMID 19948186. doi:10.1016/j.pharmthera.2009.11.005.
- ^ Lindemann L, Hoener MC. A renaissance in trace amines inspired by a novel GPCR family. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2005-05, 26 (5): 274–281. PMID 15860375. doi:10.1016/j.tips.2005.03.007.
- ^ Wang X, Li J, Dong G, Yue J. The endogenous substrates of brain CYP2D. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2014-02-05, 724: 211–218. PMID 24374199. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2013.12.025.
The highest level of brain CYP2D activity was found in the substantia nigra ... The in vitro and in vivo studies have shown the contribution of the alternative CYP2D-mediated dopamine synthesis to the concentration of this neurotransmitter although the classic biosynthetic route to dopamine from tyrosine is active. ... Tyramine levels are especially high in the basal ganglia and limbic system, which are thought to be related to individual behavior and emotion (Yu et al., 2003c). ... Rat CYP2D isoforms (2D2/2D4/2D18) are less efficient than human CYP2D6 for the generation of dopamine from p-tyramine. The Km values of the CYP2D isoforms are as follows: CYP2D6 (87–121 μm) ≈ CYP2D2 ≈ CYP2D18 > CYP2D4 (256 μm) for m-tyramine and CYP2D4 (433 μm) > CYP2D2 ≈ CYP2D6 > CYP2D18 (688 μm) for p-tyramine