克卜勒22b
| 太陽系外行星 | 太陽系外行星列表 | |
|---|---|---|
 | ||
| 母恆星 | ||
| 母恆星 | 开普勒22 | |
| 星座 | 天鵝座 | |
| 距離 | 620[1] ly (190[2] pc) | |
| 光譜類型 | G5V | |
| 軌道參數 | ||
| 半長軸 | (a) | 0.849 ± 0.018[1] AU |
| 公轉週期 | (P) | 289.862 ± 0.02日[1][3] d |
| 軌道傾角 | (i) | 89.764 +0.042 −0.025[1][4]° |
| 物理性质 | ||
| 质量 | (m) | < 0.11[4] MJ |
| 半径 | (r) | 2.4 [5] R🜨 |
| 辐射功率 | (F⊙) | 1.09 🜨 |
| 温度 | (T) | 295[5] K |
| 發現 | ||
| 發現時間 | 2009年首次觀測到[6][7] 2011年12月5日宣布發現[7] | |
| 發現者 | 开普勒太空望遠鏡科學團隊 | |
| 發現方法 | 凌日法 | |
| 發現地點 | 開普勒太空望遠鏡 | |
| 發表論文 | 已出版論文 | |
| 其他名稱 | ||
| 數據庫參考 | ||
| 太陽系外行星 百科全書 | data | |
| SIMBAD | data | |
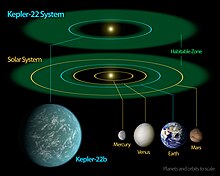
开普勒22b(英語:Kepler-22b)是NASA开普勒太空望遠鏡所發現第一個位於類太陽恆星適居帶的太陽系外行星[7][8][9]。克卜勒22b位於天鵝座內,距離地球600光年,環繞著類太陽恆星克卜勒22公轉[7][8][9]。
發現
编辑該顆行星的發現公布於2011年12月5日[8]。該行星最早于2009年的科學任務開始後第三天被开普勒太空望遠鏡偵測到。[10]並在2010年下半年觀測到它第三次凌日現象。額外的確認資料由史匹哲太空望遠鏡和地面望遠鏡提供。該行星的半徑大約是地球的2.4倍(海王星半徑60%),距離地球約600光年。該行星環繞光譜類型G型的恆星开普勒22[7][8]。
過去的凌日日期
编辑| 克卜勒22b凌日 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 凌日日期[6] | 註釋 | ||||
| 2009年5月15日 | 首次被开普勒太空望遠鏡觀察到的凌日 | ||||
| 2010年3月1日 | 由史匹哲太空望遠鏡觀察得到 | ||||
| 2010年12月15日 | 第3次被开普勒太空望遠鏡觀察到的凌日 | ||||
| 2011年10月1日 | 由史匹哲太空望遠鏡觀察得到,長7.4小時,正式確認行星的存在 | ||||
組成和結構
编辑至今其確切質量和表面成分仍不清楚[7][8]。如果其密度和地球相當(5.515 g/cm3),則質量可能是地球的13.8(2.43)倍[calc 1],表面重力是地球的2.4倍[calc 2]。如果其密度和液態水相當(1 g/cm3),其質量是地球的 2.5 倍[calc 3],表面重力是地球的0.43倍[calc 4][6]。該行星可能會被歸類為超級地球,但要視其實際質量而定[8][11]。
據估計該行星質量可能達到地球35倍,類似天王星和海王星。[12]它有可能是地球10倍質量的海洋行星[13],但也可能因為其灼熱表面而成為「超級金星」(Super Venus)。[11]
由於开普勒22b體積比地球大,它的成分可能和地球有所不同,視質量推測其外殼可能是以液體或氣體為主。它有可能是超級地球或熱海王星[8][13],其性質可能類似於半徑相近的GJ 1214 b。[14]
生命存在的可能性
编辑开普勒22b距離其母恆星的距離比地球距離太陽少15%。軌道半徑是地球軌道的85%[1],公轉周期289.9地球日[15][16]。
從开普勒22b的母星所發射出的光能量比太陽少25%[8]。距離和光能量的狀態組合在一起就是行星表面適合生命生存的適當溫度。科學家預測如果該行星無大氣層,其表面平衡溫度大約是-11 °C。如果有類似地球因為大氣層造成的溫室效應,該行星表面的溫度大約是22 °C[7][8]。
要注意的是,开普勒22b可能因為其體積過大而難以存在生命。其狀態可能比較不像地球,反而較接近海王星,擁有一個岩石核心和液體與氣體混合的表面,或者完全是液態海洋的表面。無論如何,該計畫的其中一位科學家娜塔莉·巴塔爾哈(Natalie Batalha)推測生物不無可能存在於這樣的海洋之中[17]。該行星存在生命的可能性激勵了SETI將執行的研究中把开普勒22b列為優先選項[18]。
| 溫度比較 | 金星 | 克卜勒22 | 地球 | 火星 |
| 環球平衡溫度 | 307 K 34 °C 93 °F |
262 K −11 °C 11.9 °F |
255 K −18 °C −0.4 °F |
206 K −67 °C −88.6 °F |
| + 金星的 溫室效應 |
737 K 464 °C 867 °F |
733 K 460 °C 860 °F |
||
| + 地球的 溫室效應 |
295 K 22 °C 71.6 °F |
288 K 15 °C 59 °F |
||
| + 火星的 溫室效應 |
210 K −63 °C −81 °F | |||
| 潮汐鎖定 | 幾乎 | 不太可能 | 沒有 | 沒有 |
| 環球球面反照率 | 0.9 | 未知 | 0.29 | 0.25 |
| 參考:[5][19][20][21][22][23] | ||||
參見
编辑注釋:計算
编辑參考資料
编辑- ^ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 Notes for Planet Kepler-22 b. Extrasolar Planet Database. [6 December 2011]. (原始内容存档于2012-05-05).
- ^ Notes for Planet Kepler-22 b. Extrasolar Planet Database. [6 December 2011]. (原始内容存档于2012-05-05).
- ^ Klotz, Irene (5 December 2011) Alien Planet Could Host Life, 探索頻道
- ^ 4.0 4.1 Planet: Kepler-22 b. The Extrasolar Planet Encyclopedia. [14 December 2011]. (原始内容存档于2012-05-05).
- ^ 5.0 5.1 5.2 "NASA Telescope Confirms Alien Planet in Habitable Zone" (页面存档备份,存于互联网档案馆). Space.com. 12 May 2011
- ^ 6.0 6.1 6.2 Borucki, William J.; Koch, David G.; Batalha, Natalie; Bryson, Stephen T.; Rowe, Jason; Fressin, Francois; Torres, Guillermo; Caldwell, Douglas A.; Christensen-Dalsgaard, Jørgen; Cochran, William D.; Devore, Edna; Gautier, Thomas N.; Geary, John C.; Gilliland, Ronald; Gould, Alan; Howell, Steve B.; Jenkins, Jon M.; Latham, David W.; Lissauer, Jack J.; Marcy, Geoffrey W.; Sasselov, Dimitar; Boss, Alan; Charbonneau, David; Ciardi, David; Kaltenegger, Lisa; Doyle, Laurance; Dupree, Andrea K.; Ford, Eric B.; Fortney, Jonathan; Holman, Matthew J. Kepler-22b: A 2.4 Earth-radius Planet in the Habitable Zone of a Sun-like Star. The Astrophysical Journal. 2012, 745 (2): 120. arXiv:1112.1640 . doi:10.1088/0004-637X/745/2/120. The article gives Julian dates, which are converted at imcce.fr (页面存档备份,存于互联网档案馆) (all dates in Univ. Time)
- ^ 7.0 7.1 7.2 7.3 7.4 7.5 7.6 NASA – NASA's Kepler Confirms Its First Planet in Habitable Zone of Sun-like Star. NASA Press Release. [6 December 2011]. (原始内容存档于2013-06-07).
- ^ 8.0 8.1 8.2 8.3 8.4 8.5 8.6 8.7 8.8 Kepler 22-b: Earth-like planet confirmed. BBC Online. 5 December 2011 [6 December 2011]. (原始内容存档于2019-08-27).
- ^ 9.0 9.1 Kepler-22b: Facts About Exoplanet in Habitable Zone. [2014-01-05]. (原始内容存档于2017-06-07).
- ^ Dr. Tony Phillips. Kepler Confirms First Planet in Habitable Zone of Sun-like Star. NASA science news. 5 December 2011 [31 January 2012]. (原始内容存档于2013-11-12).
- ^ 11.0 11.1 Kepler-22b - NASA. [2013-12-08]. (原始内容存档于2017-03-31).
- ^ gives the definition of "Neptunian", among others.. [2012-01-24]. (原始内容存档于2012-09-11).
- ^ 13.0 13.1 Abel Mendez Torres. Updates on Exoplanets during the First Kepler Science Conference. Planetary Habitability Laboratory at 波多黎各大學阿雷西沃分校. 2011-12-08 [2011-12-08]. (原始内容存档于2011-12-08).
- ^ Charbonneau, David; Zachory K. Berta; Jonathan Irwin; Christopher J. Burke; Philip Nutzman; Lars A. Buchhave; Christophe Lovis; Xavier Bonfils; David W. Latham; Stéphane Udry; Ruth A. Murray-Clay; Matthew J. Holman; Emilio E. Falco; Joshua N. Winn; Didier Queloz; Francesco Pepe; Michel Mayor; Xavier Delfosse; Thierry Forveille. A super-Earth transiting a nearby low-mass star. Nature. 2009, 462 (17 December 2009): 891–894 [2009-12-15]. doi:10.1038/nature08679. (原始内容存档于2010-01-15).
- ^ alien planet found in habitable zone - discovery. [2011-12-05]. (原始内容存档于2012-01-07).
- ^ NASA's Kepler Mission Confirms Its First Planet in Habitable Zone of Sun-like Star - NASA. [2011-12-05]. (原始内容存档于2015-06-12).
- ^ Borenstein, Seth. Planet in sweet spot of Goldilocks zone for life. Associated Press. 5 December 2011 [6 December 2011]. (原始内容存档于2012-09-05).
- ^ Ian O'Neill. SETI to Hunt for Aliens on Kepler's Worlds. Discovery News. 2011-12-05 [2011-12-10]. (原始内容存档于2012-12-25).
- ^ Vogt, Steven S.; Butler, R. Paul; Rivera, Eugenio J.; Haghighipour, Nader; Henry, Gregory W.; Williamson, Michael H. The Lick-Carnegie Exoplanet Survey: A 3.1 M_Earth Planet in the Habitable Zone of the Nearby M3V Star Gliese 581. 29 September 2010. arXiv:1009.5733 [astro-ph.EP].
- ^ Stephens, Tim. Newly discovered planet may be first truly habitable exoplanet. University News & Events. 加利福尼亞大學聖塔克魯茲分校. 29 September 2010 [2013-12-08]. (原始内容存档于2013-11-03).
- ^ NASA, Mars: Facts & Figures. [28 January 2010]. (原始内容存档于2010-05-28).
- ^ Mallama, A.; Wang, D.; Howard, R. A. Venus phase function and forward scattering from H2SO4. Icarus. 2006, 182 (1): 10–22. Bibcode:2006Icar..182...10M. doi:10.1016/j.icarus.2005.12.014.
- ^ Mallama, A. The magnitude and albedo of Mars. Icarus. 2007, 192 (2): 404–416. Bibcode:2007Icar..192..404M. doi:10.1016/j.icarus.2007.07.011.
- ^ Kipping, D. M.; Forgan, D.; Hartman, J.; Nesvorný, D.; Bakos, G. Á.; Schmitt, A.; Buchhave, L. The Hunt for Exomoons with Kepler (Hek). Iii. The First Search for an Exomoon Around a Habitable-Zone Planet. The Astrophysical Journal. 2013, 777 (2): 134. arXiv:1306.1530v1 . doi:10.1088/0004-637X/777/2/134.
外部連結
编辑- YouTube上的Kepler-22b - First Discovered Planet In Habitable Zone
- "NASA Telescope Confirms Alien Planet in Habitable Zone"(页面存档备份,存于互联网档案馆) (Space.com)
- "Kepler 22-b: Earth-like planet confirmed"(页面存档备份,存于互联网档案馆) (BBC)
- "NASA's Kepler Confirms Its First Planet In Habitable Zone"(页面存档备份,存于互联网档案馆) (NASA)
- Kepler discoveries: Kepler-22b "a yearly orbit of 289 days"(页面存档备份,存于互联网档案馆) (NASA)
- "View of Kepler 22-b Sky Location"(页面存档备份,存于互联网档案馆) (WorldWide Telescope)
- "The Habitable Exoplanets Catalog"(页面存档备份,存于互联网档案馆) (PHL/UPR Arecibo)